Record Lectures 3 1 35
Earth & Environmental Sciences
Open Voice Memos, Sound Recorder, or your desired app. Hold the bottom of the phone near the audio source. Tap the Record button. Tap Stop when you're finished. Name the file if prompted. Records 35-40 Summary. D-503's head is bandaged in a 'pitiless ring of glass iron' and he cannot sleep, planning U-'s murder. The taste of something 'disgustingly sweet' has him spitting into a handkerchief. He pulls out a defective piston rod he has been studying, wraps it in pages of his manuscript, and heads to the controller's table.
EES 1. Natural Disasters and Earth Resources
- This is FindLaw's hosted version of Indiana Code Title 35. Criminal Law and Procedure. Use this page to navigate to all sections within the Title 35. Criminal Law and Procedure. Expand sections by using the arrow icons.
- Record the lecture with your computer's recording program. For Apple computers, you can download a recording system called Audacity. For a PC, find the Sound Recorder program in the Start menu. Using software like Audacity lets you shorten the raw file of the lecture, which is the entire recorded lecture before any editing has been done to it.
Prerequisite: G. E. Foundation B4 (except for those with declared majors in the College of Science and Mathematics). Processes and materials that produce the different geologic resources and hazards (earthquakes, volcanoes, floods, landslides). Plate tectonic theory (including continental drift) as the unifying model to explain geologic phenomena. Emphasizes the relationship between geology and humans. G. E. Breadth B1. (3 lecture, 2 lab hours; optional field trips) (Course fee, $10).
Units: 4
Course Typically Offered: Fall, Spring
GE Area: B1
EES 1V. Natural Disasters and Earth Resources - Virtual Labs
Prerequisite: G. E. Foundation B4 (except for those with declared major in the College of Science and Mathematics). Processes and materials that produce the different geologic resources and hazards (earthquakes, volcanoes, floods, landslides). Plate tectonic theory (including continental drift) as the unifying model to explain geologic phenomena. Emphasizes the relationship between geology and humans. G. E. Breadth B1. (3 lecture, 2 lab hours; optional field trips (Course fee, $10) This course offers virtual labs with alternating in-class and self-paced lab options
Units: 4
Course Typically Offered: Fall, Spring
GE Area: B1
EES 2. Historical Geology
Prerequisites: EES 1. Origins & evolution of solid earth, life, oceans, and atmosphere as revealed by the rock record's fossil remains with emphasis on the evolution of life and the physical environment (2 lecture, 2 lab hours) (Course fee, $10)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Spring
EES 3. Geology Field Trip
Extended weekend field trip to areas of geologic interest including Yosemite National Park, Death Valley, or coastal California. May be repeated. Non-majors encouraged. CR/NC grading only. (Weekend field trips required; Field trip fee, $60)
Units: 1, Repeatable up to 3 units
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 4. Environmental Science
Prerequisite G.E. Foundation B4. Introduction to environmental science, focusing on environmental principles and processes. Topics include human population and consumption, ecosystems and biodiversity, resource management and conservation, energy sources and technology use, dynamics, ecosystems, pollution and wastes, environmental economics and ethics, global changes, and tomorrow's world. (3 lecture, 2 lab hours) (Course fee, $10)
Units: 4
Course Typically Offered: Fall, Spring
GE Area: B1
EES 9. Introduction to Earth Science
Introduction to earth science emphasizing K-6 teacher preparation. Addresses topics in earthquakes, volcanoes, rock and mineral formation, oceanography, astronomy, and meteorology. For liberal studies majors only (Course fee, $10)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall, Spring
EES 12. Mineralogy
Prerequisite: EES 1; CHEM 1A (or concurrently). Properties, relationships, uses origin of minerals; determination of common minerals by physical and other tests. Field trips may be required. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours) (Course fee, $35)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 30. Introductory Field Methods
Pre- or co-requisites: EES 1, EES 2 or instructor's permission. Introduction to geologic fieldwork methods, including use of Brunton pocket transit and stereo aerial photographs, preparation/interpretation of maps and geologic cross-sections. Graded for EES majors/minors. (1 lecture, 6 lab/field hours) (Weekend field trips required) (Course fee, $35.00)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Spring
EES 31. Environmental Sampling Methods
Prerequisites: CHEM 1A; EES 4. This course is an introduction to quantification, assessment, and prediction of environmental processes and interactions. The course will introduce students to sampling strategies and scientific procedures for addressing scientific questions. Ensuring that the procedures and strategies for data collection address defined hypotheses will be a central theme. (Formerly EES 150T)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Spring
EES 50. National Parks of the Sierra Nevada
Geology, ecology, and history (human and natural) of Yosemite, Kings Canyon, and Sequoia National Parks and issues facing these Parks. (3 lecture hours, Field Exercises required; Field trip fee, $25).
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 100. Analytical Methods in the Earth Sciences
Prerequisites: EES 12 (concurrent enrollment recommended). The course covers various methods for identifying and characterizing crystalline substances. Topics include Crystallography, Optical methods for mineral identification, and powder X-ray diffraction methods for mineral identification structure characterization. (1 lecture, 3 lab hours) (Course fee, $10)
Units: 2
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 101. Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology
Prerequisites: EES 30, EES 100; CHEM 1B (or concurrently). Origin classification, textures, structures, and geologic setting of igneous and metamorphic rocks; examination of samples in outcrop, hand specimen, and thin section. Weekend field trips required. (3 lecture, 3 lab hours) (Course fee, $35)
Units: 4
Course Typically Offered: Spring
EES 102. Sedimentology
Prerequisites: EES 30 or EES 31 (or concurrently). Origin, classifications, textures, and structures of sedimentary rocks; examination of samples in hand specimen and thin section. Required field component for field stratigraphy and sedimentology, and producing a formal field report. (3 lecture, 3 lab hours plus field project) (Course fee, $35)
Units: 4
Course Typically Offered: Spring
EES 104W. Scientific Writing and Research Techniques
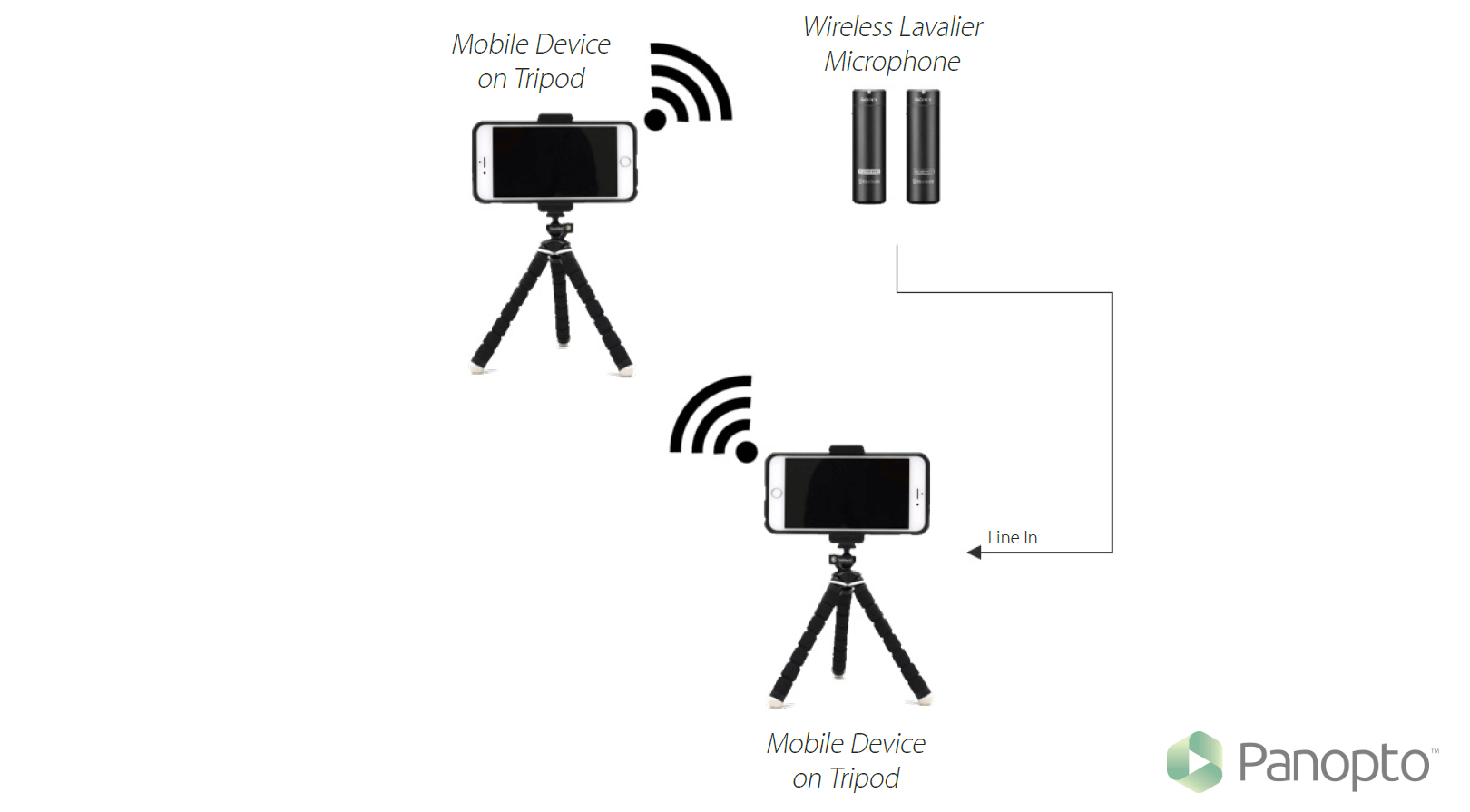
Prerequisite: EES 1 or EES 4. Organizing and writing the scientific report. Topics include: techniques and conventions in research methods, evaluation approaches, and presentation of results. Peer reviews. Oral presentation and term paper required. Meets the upper-division writing skills requirement for graduation.
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 105. Geomorphology
Prerequisite: EES 1; EES 30 or EES 31 (or concurrently). Landforms, climates, geologic processes, and their interrelation in shaping the earth's surface today and in the geologic past. Interpretation of topographic maps and aerial photographs. Field trips required. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours) (Course fee, $35)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Spring
EES 106. Structural Geology
Prerequisites: EES 30, EES 101; MATH 75 (or concurrently), PHYS 2A. Recognition, representation, and interpretation of structural features of the earth's crust. Includes theoretical and mechanical principles. Study of regional tectonics and major structural provinces of the Cordillera. Required field component for field mapping, collectiing and producing formal field report. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours plus field project) (Course fee, $35)
Units: 4
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 107. Advanced Field Methods
Prerequisites: EES 102, EES 104, EES 106. Field trips to areas of diverse geology; observation, description, and mapping of geologic phenomena. Includes written reports of areas selected for study. Students should contact the department for details. (9 lab hours usually including fieldwork on weekends or during January intercession and spring vacation) (Course fee, $35)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Spring
EES 108. Soil and Water Sciences
Prerequisites: BIOL 1A, CHEM 1B and 1BL, EES 1 or EES 4, PHYS 2A or PHYS 4A and 4AL, MATH 75. Introduction to the physical, chemical, and biological properties of soil and water in relation to environmental sustainability. Introduction to the hydrologic cycle, distribution of soil and water sources. Discussion of soil and water resources management and policy issues. (3 lecture, 3 lab hours; optional field trips) (Course fee, $10)
Units: 4
Course Typically Offered: Spring
EES 109. Atmospheric Science
Prerequisites: BIOL 1A, CHEM 1B and 1BL, EES 1 or EES 4, PHYS 2A or PHYS 4A and 4AL, MATH 75. The structure of the atmosphere and man's impact upon it. The causes and consequences of air pollution. Air quality standards. Stratospheric and tropospheric ozone. Introduction to the chemistry of air pollution and air pollution control strategies. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours; optional field trips) (Course fee, $10)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 110. Invertebrate Paleontology
Prerequisites: EES 1 or BIOL 1A and BIOL 1B, or BIOL 12, or BIOL 11. Invertebrate structures and development of prehistoric animals; introduction to stratigraphic importance of fossils. Field trips may be required. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours) (Course fee, $10)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 112. Planet Earth through Time
Credit not allowed after completion of EES 2. Prerequisite: G.E. Foundation and Breadth Area B. Principles of geology used in the interpretation of the history of Earth as revealed in rocks and their fossils. Includes origin of the solar system, evolution of atmosphere and oceans, origin of life, rise and fall of the dinosaurs, plate tectonics,and ice ages. G. E. Integration IB. Does not satisfy Division 1 pre-1999 G. E. curriculum.
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall, Spring
GE Area: IB
EES 113. Stream Habitat Restoration
Prerequisites: EES 1 or BIOL 10 or BIOL 1A or instructor's consent. Investigation of stream geology, hydrology, and biology relevant to restoring stream habitat. Includes collecting and interpreting lab and field data. Field trips required. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours)
Units: 3
EES 114. Engineering Geology

Prerequisites: EES 1 and MATH 5 or MATH 72 or MATH 75 or MATH 75A and MATH 75B. Introduction to techniques and theory of geotechnical investigations. Includes field and lab techniques in soil and rock mechanics, rock logging, geophysics, slope stability, engineering hydrogeology, stereo analysis, seismic engineering. Recommended for students in geology or civil engineering. Field trips required. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours) (Course fee, $35)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 117. Hydrogeology
Prerequisites: EES 1 or EES 4; MATH 75 or MATH 75A and 75B. Recommended courses: EES 124 and MATH 76. The hydrologic cycle; surface water processes; stream flow and hydrograph; properties of porous geologic materials; principles of groundwater flow; water wells; geology of groundwater occurrence; water quality and pollution. Field trip required. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours) (Course fee, $35)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 118. Applied Geophysics
Prerequisites: EES 1, PHYS 2A and completion of or concurrent enrollment in PHYS 2B. Presents an overview of geophysics as applied to problems in exploration, engineering, and environmental geology. Emphasizes hands-on methods of data acquisition and interpretation that entry-level geologists will most likely encounter including gravity, magnetics, seismic refraction, ground penetrating radar, down-hole surveys, andelectrical resistivity. Field in strumentation is used throughout. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours) (Course fee, $35)
Units: 3
EES 122. Stratigraphy
Prerequisites: EES 102 (may be taken concurrently). Stratigraphic principles and recognition of stratigraphic units. Emphasis on tectonostratigraphic concepts. (2 lecture, 3 lab/field hours) (Course fee, $35)
Units: 3
EES 124. Geochemistry
Prerequisites: CHEM 1A and CHEM 1B and EES 1 or EES 15; EES 12 and EES 101 recommended. Chemistry applied to earth processes and evolution. Reactions involved in origin and transformations of natural waters, rocks, and minerals. Crystal chemistry and behavior of elements and isotopes. (3 lecture hours) (Formerly GEOL 124)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 125. Global Paleoclimates
Prerequisites: EES 1 and either MATH 2, MATH 5, or MATH 75. Introduction to processes and mechanisms behind gradual and abrupt climate change over the last 500 million years. Discussion of investigation methods in paleobiology, paleogeography, and paleoceanography. Proxies interpretation for building age models and correlation of marine and terrestrial records.
Units: 3
EES 130T. Advanced Problems in Geology
Prerequisite: senior standing in geology. Topics or problems in the following fields: engineering geology, geology of North America, field geology, micropaleontology, advanced ground water geology, sedimentation and sedimentary rocks, geochemistry, geophysics, volcanic geology and marine geology. Some topics may have labs.
Units: 1-3, Repeatable up to 6 units
EES 135W. Dinosaurs
Prerequisite: satisfactory completion (C or better) of the ENGL 5B or ENGL 10 graduation requirement, to be taken no sooner than the term in which 60 units are completed. Introduction to the dinosaurs as revealed from sedimentary rocks and fossils, including their evolution, diversity, habitats, extinction, and fossilization. Develops skills for scientific writing of proposals, abstracts, journal articles, and reviews. Meets the upper-division writing skills requirement for graduation (3 lecture hours)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall, Spring
EES 150T. Studies in Earth Science
Applicable to the geology major only with prior departmental approval. Prerequisite: EES 1. Earth science topics designed for students minoring in geology, with an interest in earth science, in teacher training, and for elementary and secondary teachers.
Units: 1-3, Repeatable up to 6 units
EES 154. Introductory Earth Science
Not applicable to the B.S. in Geology. Appropriate for liberal studies majors and K-6 teachers. Earth systems interactions demonstrated through hands-on activities, experiments, and field work. Topics include recognition, origin, and use of rocks and minerals; geologic timeand fossils; interpretation of landscapes and the rock record; and plate tectonics. (2 lecture, 2 lab hours, 1 hour arranged) (Course fee, $10)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Spring
EES 155. Discovering Earth Science
Not applicable to the B.S. in Geology. Prerequisites: EES 1, or EES 112, or instructor's permission. Appropriate for students and 7-12 teachers seeking a secondary school science credential. Activity-based discovery of earth science and its integration with other sciences. Topics include energy in the earth system, geochemical cycles, dynamic interactions between the lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere, and origin/evolution of the earth. (2 lecture, 2 lab hours, 1 hour arranged) (Course fee, $10)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Spring
EES 160. Field Studies
Prerequisite may be specified by instructor. Field trips during weekends or winter/spring recess to geologically important and significant areas such as the Grand Canyon, Baja California, the Sierra Nevada, Death Valley.
Units: 1-4
EES 167. Oceans and Atmosphere and Climate
Prerequisite: G. E. Foundation and Breadth Area B. Integrated introduction to oceans, and atmosphere, and climate changes: their origin and evolution; plate tectonics; ocean currents, waves, and tides; atmospheric circulation and El Nino; production and life; and environmental issues and concerns. G.E. Integration IB.
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall, Spring
GE Area: IB
EES 168. California's Earth System
Prerequisites: G. E. Foundation and Breadth Area B. Not applicable to B.S. in Geology. Interaction of earth, water, air, and life in California's earth system over geologic time. Human interaction with the environment. G.E. Integration IB.
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall, Spring
GE Area: IB
EES 177. Quantitative Methods for Earth Science
Prerequisites: EES 1; MATH 75. Applications of mathematical techniques and quantitative methods in earth science; introduction to basic skills, including statistical methods, numerical techniques, matrix operations, and spatial analysis. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours)
Units: 3
EES 178. Geostatistics
Prerequisites: EES 1 or EES 4; Math 75 recommended. Principles and application of geostatistics and visualization techniques in Geo-environmental sciences. Topics include spatial and temporal correlation, variograms, kriging, and factor analysis, etc. Techniques are used for evaluation of mineral deposits and characterization of an environment with limited sampling data. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours, 1 day required field tests).
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 180. Computer Applications in Geology
How To Record Online Lecture
Use of computers in geology, focusing on such applications as multi-dimensional graphics, desktop mapping, communications, on-line resources, modeling. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours)
Units: 3
EES 185. Remote Sensing for the Natural Sciences
Prerequisite: General Education Breadth, Area B; GEOG 105 recommended. Introduction to remote sensing techniques, including ultraviolet, visible, and infrared electromagnetic sensors, both space and aircraft based, and acoustic methods. Laboratory exercises will use examples from geology, agriculture, and society. familiarity with computers required. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours)
Units: 3
EES 186. Environmental GIS
Prerequisite: GEOG 107 recommended. Spatial information management, analysis, interpretation, and display using computer methods. Map concepts, spatial relationships, database design, and spatial analysis of data. Laboratory exercises using geologic map data, faults, earthquake epicenters, stream habitats and restoration, and endangered species. Familiarity with computers required. (2 lecture, 3 lab hours)
Units: 3
Course Typically Offered: Fall
EES 187. Biogeochemistry
Prerequisites: CHEM 1A and 1AL, 1B and 1BL; BIOL 1A, 1B and 1BL; PHYS 2A or PHYS 4A and 4AL; EES 124; MATH 75. Comprehensive understanding of the processes that alter the surface of the Earth drawing on the foundational principles of biology, chemistry, and geology. Reactions that reshape modern earth are facilitated by biological, geological, and chemical interaction whose timescale is critical to understanding significance and connectedness to other reactions and cycles. (3 lecture, 3 lab hours)
Units: 4
EES 190. Independent Study
See Academic Placement - Independent Study. Approved for RP grading.
Units: 1-3, Repeatable up to 6 units
Course Typically Offered: Fall, Spring
EES 191. Environmental Science Capstone
Prerequisites: EES 124, EES 104W. This course surveys significant environmental challenges facing our local communities. We will evaluate scientific inquiry and investigation of environmental questions and design projects that attempt to seek solutions. Students will complete as degree. Approved for RP grading.
Units: 2-6
EES 299C. Thesis Continuation
Pre-requisite: Thesis EES 299. For continuous enrollment while completing the thesis. May enroll twice with department approval. Additional enrollments must be approved by the Dean of Graduate Studies.
Units: 0
-->In Microsoft Teams, users can record their Teams meetings and group calls to capture audio, video, and screen sharing activity. There is also an option for recordings to have automatic transcription, so that users can play back meeting recordings with closed captions and search for important discussion items in the transcript. The recording happens in the cloud and is saved to Microsoft Stream, so users can share it securely across their organization.
Related: Teams meeting recording end user documentation
Note
The change from using Microsoft Stream to OneDrive for Business and SharePoint for meeting recordings will be a phased approach. For detailed information on each phase, see Use OneDrive for Business and SharePoint or Stream for meeting recordings.
Note
For information about using roles in Teams meetings, and how to change users' roles, see Roles in a Teams meeting.
Prerequisites for Teams cloud meeting recording
For a Teams user's meetings to be recorded, Microsoft Stream must be enabled for the tenant. In addition, the following prerequisites are required for both the meeting organizer and the person who is initiating the recording:
- User has Office 365 E1, E3, E5, A1, A3, A5, Microsoft 365 Business Premium, Business Standard, or Business Basic1
- User has consented to the company guidelines, if set up by the admin
- User has sufficient storage in Microsoft Stream for recordings to be saved
- User has CsTeamsMeetingPolicy -AllowCloudRecording setting set to true in order to record meetings and group calls
- User has CsTeamsCallingPolicy -AllowCloudRecordingForCalls setting set to true in order to record 1:1 calls
- User is not an anonymous, Guest, or federated user in the meeting
- To enable transcription for a user's meeting, the Teams meeting policy they are assigned to must have the -AllowTranscription setting set to true.
1 As of August 20, 2020, access to the meeting recording file will expire after 21 days for users with A1. For more information, see Upload a Microsoft Teams meeting recording to Stream.
Important
Users won't need a Microsoft Stream license assigned if you want users to only record and download the recordings. This will mean that the recordings aren't stored in Microsoft Stream but are instead stored in Async Media Services (AMS) with a 21-day limit before it's deleted. It's not something at this point that an admin can control or manage including the ability to delete it.
Important
Also note, for recordings that are on AMS, the recording retention is affected by the chat message itself. As such, any deletion of the original AMS Recording chat message will prevent users from being able to access the recording. There are two scenarios that can affect this. 1) User manually deletes the chat message - In this scenario, as the original message is gone, users will no longer be able to access the recording and no further downloads will be possible. However, the recording itself may still be retained within Microsoft's internal systems for a time (not exceeding the original 21-day period). 2) Recording chat message is deleted by chat retention policy - AMS Recordings are directly tied to the chat retention policy. As such, although recordings on AMS will by default be retained for 21 days before being deleted, if the chat message is deleted before the 21-day time period, due to chat message retention policies, the recording will also be deleted. There is no way to recover the recording after this.
Set up Teams cloud meeting recording for users in your organization
This section explains how you can set up and plan for recording Teams meetings.
Turn on Microsoft Stream for users in the organization
Microsoft Stream is available as part of eligible Microsoft 365 and Office 365 subscriptions or as a standalone service. See the Stream licensing overview for more details. Microsoft Stream is now included in Microsoft 365 Business, Microsoft 365 Business Standard, and Microsoft 365 Business Basic.
Learn more about how you can assign licenses to users in Microsoft 365 or Office 365 so that users can access Microsoft Stream. Ensure that Microsoft Stream is not blocked for the users, as defined in Block sign-ups for Microsoft Stream.
Make sure users have upload video permissions in Microsoft Stream
By default, everyone in the company can create content in Stream, once Stream is enabled and the license is assigned to the user. A Microsoft Stream administrator can restrict employees for creating content in Stream. The users who are in this restricted list will not be able to record meetings.
Notify employees to consent to company guidelines in Microsoft Stream
If a Microsoft Stream administrator has set up company guideline policy and requires employees to accept this policy before saving content, users must do so before recording in Microsoft Teams. Before you roll out the recording feature in the organization, make sure users have consented to the policy.
Turn on or turn off cloud recording
You can use the Microsoft Teams admin center or PowerShell to set a Teams meeting policy to control whether user's meetings can be recorded.
In the Microsoft Teams admin center, turn on or turn off the Allow cloud recording setting in the meeting policy. To learn more, see Manage meeting policies in Teams.
Using PowerShell, you configure the AllowCloudRecording setting in TeamsMeetingPolicy. To learn more, see New-CsTeamsMeetingPolicy and Set-CsTeamsMeetingPolicy.
Note that both the meeting organizer and the recording initiator need to have the recording permissions to record the meeting. Unless you have assigned a custom policy to the users, users get the Global policy, which has AllowCloudRecording enabled by default.
Note
For more information about using Teams roles to configure who has permission to record a meeting, see Roles in a Teams meeting.
For a user to fall back to the Global policy, use the following cmdlet to remove a specific policy assignment for a user:
To change value of AllowCloudRecording in the Global policy, use the following cmdlet:
| Scenario | Steps |
|---|---|
| I want all users in my company to be able to record their meetings |
|
| I want the majority of my users to be able to record their meetings but selectively disable specific users who are not allowed to record |
|
| I want recording to be 100% disabled |
|
| I want recording to be turned off for the majority of the users but selectively enable specific users who are allowed to record |
|
Where your meeting recordings are stored
Meeting recordings are stored in Microsoft Stream cloud storage. Currently, the meeting recording feature is turned off for customers whose Teams data is stored in-country if Microsoft Stream isn't available in the in-country data residency region where the data is stored. The meeting recording feature can be turned on for customers whose data is supposed to be stored in-country even if Microsoft Stream isn't available in the in-country data residency region. This can be done by allowing recordings to be stored in the nearest geographic region for Microsoft Stream.
If your Teams data is stored in-country and you prefer to store meeting recordings in-country, we recommend that you turn off the feature, and then turn it on after Microsoft Stream is deployed to your in-country data residency region. To turn off the feature for all users in your organization, turn off the Allow cloud recording setting in the Global Teams meeting policy, which is in the Microsoft Teams admin center. If, however, you still wish to enable recordings to be stored in the nearest geographic region for Microsoft Stream, you must turn on both Allow cloud recording and Allow Recording Storage Outside Region before this change takes place.
To enable recordings in-region in the Global policy, use the following cmdlet:
Here's a summary of what happens when you turn on meeting recording when this change takes effect:
Record Lectures 3 1 35 Minutes
| If you turn on meeting recordings... | Meeting recordings are stored... |
|---|---|
| Before Microsoft Stream is available in your in-country data residency region | In the nearest Microsoft Stream region |
| After Microsoft Stream is available in your in-country data residency region | In your in-country data residency region |
For new and existing tenants that haven't yet turned on meeting recording, new recordings are stored in-country after Microsoft Stream is available in the in-country data residency region. However, any tenant that enables meeting recording before Microsoft Stream is available in the in-country data residency region will continue to use the Microsoft Stream storage for existing and new recordings, even after Microsoft Stream is available in the in-country data residency region.
To find the region where your Microsoft Stream data is stored, in Microsoft Stream, click ? in the upper-right corner, click About Microsoft Stream, and then click Your data is stored in. To learn more about the regions where Microsoft Stream stores data, see Microsoft Stream FAQ.
To learn more about where data is stored across services in Microsoft 365 or Office 365, see Where is your data located?
Turn on or turn off recording transcription
This setting controls whether captions and transcription features are available during playback of meeting recordings. If you turn this off, the Search and CC options won't be available during playback of a meeting recording. The person who started the recording needs this setting turned on so that the recording also includes transcription.
Note
That transcription for recorded meetings is currently only supported for users who have the language in Teams set to English and when English is spoken in the meeting. They are stored together with the meeting recordings in Microsoft Stream cloud storage.
You can use the Microsoft Teams admin center or PowerShell to set a Teams meeting policy to control whether the recording initiator gets a choice to transcribe the meeting recording.
In the Microsoft Teams admin center, turn on or turn off the Allow transcription setting in the meeting policy. To learn more, see Manage meeting policies in Teams.
Using PowerShell, you configure the AllowTranscription setting in TeamsMeetingPolicy. To learn more, see New-CsTeamsMeetingPolicy and Set-CsTeamsMeetingPolicy.
Unless you have assigned a custom policy to the users, users get the Global policy, which has AllowTranscription disabled by default.
For a user to fall back to Global policy, use the following cmdlet to remove a specific policy assignment for a user:
To change value of AllowCloudRecording in the Global policy, use the following cmdlet:
| Scenario | Steps |
|---|---|
| I want all users in my company to be able to transcribe when initiating recording of a meeting |
|
| I want the majority of my users to be able to transcribe the meeting recordings, but selectively disable specific users who are not allowed to transcribe |
|
| I want transcription of the recording to be 100% disabled |
|
| I want transcription to be disabled for the majority of the users but selectively enable specific users who are allowed to transcribe |
|
Planning for storage
The size of a 1-hour recording is 400 MB. Make sure you understand the capacity required for recorded files and have sufficient storage available in Microsoft Stream. Read Microsoft Stream Licensing overview to understand the base storage included in the subscription and how to purchase additional storage.
Manage meeting recordings
The meeting recordings are considered tenant-owned content. If the owner of the recording leaves the company, the admin can open the recording video URL in Microsoft Stream in admin mode. The admin can delete the recording, update any recording metadata, or change permissions for the recording video. Learn more about admin capabilities in Stream.
Note
See Manage user data in Microsoft Stream and Permissions and privacy in Microsoft Stream for additional information on managing recordings and user access.
Compliance and eDiscovery for meeting recordings
The meeting recordings are stored in Microsoft Stream, which is Microsoft 365 and Office 365 Tier-C compliant. To support e-Discovery requests for compliance admins who are interested in meeting or call recordings for Microsoft Streams, the recording completed message is available in the compliance content search functionality for Microsoft Teams. Compliance admins can look for the keyword 'recording' in the subject line of the item in compliance content search preview and discover meeting and call recordings in the organization. A prerequisite for them to view all recordings is that they will need to be set up in Microsoft Stream with admin access. Learn more about assigning admin permissions in Stream.